Arachis genetic resources: evaluation of peanut smut resistance in wild species
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.48162/rev.39.164Palabras clave:
Thecaphora frezii, Arachis hypogaea, maníes silvestres, resistencia, genomasResumen
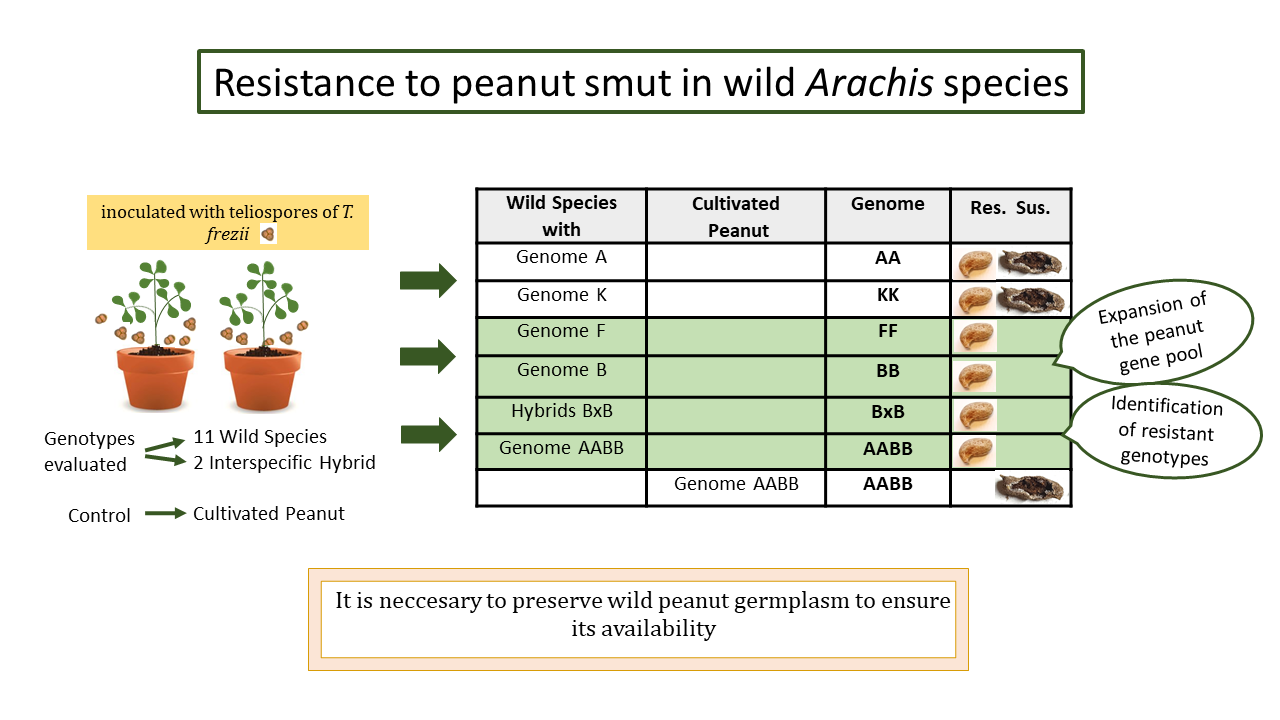
Genetic resources are essential for crop improvement. Particularly, wild species related to peanuts are an important source of resistance to various factors. Thecaphora frezii, a pathogen causing peanut smut, leads to yield losses in Argentina’s peanut sector up to 35%. This study evaluated the response of 11 diploid species with A, B, F and K genomes, A. monticola (AABB), and diploid interspecific hybrids (BB), to T. frezii over two cropping seasons. Plants were grown in 20L pots (three replicates each) under field conditions and inoculated with teliospores of the pathogen (20,000 tel./g of soil). The disease was quantified through incidence (% of diseased pods) and severity (scale from 0 to 4). Among A genome species, A. duranensis exhibited the highest incidence at 15.27%; for K genome species, A. batizocoi reached 13.18%. Resistance to T. frezii was observed in the wild species A. diogoi and A. stenosperma (A genome), A. williamsii (B genome), A. trinitensis (F genome), A. cruziana (K genome), and the intragenomic hybrids, constituting new records. Our findings expand the peanut gene pool information for breeders and identify resistant genotypes, supporting the need to preserve wild peanut germplasm to ensure its availability.
Highlights:
- Arachis species with B and F genomes displayed resistance to peanut smut, while AA and KK genome species exhibited varying susceptibility.
- Genotypes resistant to Tecaphora frezii were identified, expanding the peanut gene pool available for developing resistant genotypes.
- Wild Arachis species constitute important sources of alleles to diversify A. hypogaea genome and enhance resistance to multiple diseases, including peanut smut.
- Careful conservation of wild groundnut germplasm is crucial to ensure its availability for future breeding efforts.
Descargas
Citas
Arias, S. L.; Mary, V. S.; Velez, P. A.; Rodriguez, M. G.; Otaiza-Gonzalez, S. N.; Theumer, M. G. 2021. Where does the peanut smut pathogen, Thecaphora frezii, ft in the spectrum of smut diseases? Plant Dis. 105(9): 2268-2280. doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-11-20-2438-FE
Astiz Gassó, M.; Leis, R.; Marinelli, A. 2008. Evaluación de incidencia y severidad del carbón de maní (Thecaphora frezii) en infecciones artificiales, sobre cultivares comerciales de maní. Actas 1° Congreso Argentino de Fitopatología. Córdoba. http://aafitopatologos.com.ar/wp/wp-content/uploads/2014/11
Astiz Gassó, M.; Leis, R.; Marinelli, A. 2011. Evaluación de la tolerancia del germoplasma de maní (Arachis spp.) para el manejo del carbón Thecaphora frezii. Actas XXVI Jornada Nacional del maní. Argentina.
Ballen-Taborda, C.; Chu, Y.; Ozias-Akins, P.; Timper, P.; Holbrook, C. C.; Jackson, S. A.; Bertioli, D. J.; Bertioli, S. C. M. 2019. A new source of root-knot nematode resistance from Arachis stenosperma incorporated into allotetraploid peanut (Arachis hypogaea). Scientific Reports. 9: 17702. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-54183-1
Bertioli, D. J.; Cannon, S. B.; Froenicke, L.; Huang, G.; A. D. Farmer, E. K. S. Cannon; Liu, X.; Gao, D.; Clevenger, J.; Dash, S.; Ren, L.; Moretzsohn, M. C.; Shirasawa, K.; Huang, W.; Vidigal, B.; Abernathy, B.; Chu, Y.; Niederhuth, C. E.; Umale, P.; Araújo, A. C. G.; Kozik, A.; Do Kim, K.; Burow, M. D.; Varshney, R. K.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Barkley, N.; Guimarães, P. M.; Isobe, S.; Guo, B.; Liao, B.; Stalker, H. T.; Schmitz, R. J; Scheffler, B. E.; Leal-Bertioli, S. C. M.; Xum, X.; Jackson, S. A.; Michelmore, R.; Ozias-Akins, P. 2016. The genome sequences of Arachis duranensis and Arachis ipaënsis, the diploid ancestors of cultivated peanut. Nat. Genet. 48: 438-446. doi:10.1038/ng.3517
Bertioli, D. J.; Jenkins, J.; Clevenger, J.; Dudchenko, O.; Gao, D.; Seijo, G.; Leal-Bertioli, S. C. M.; Ren, L.; Farmer, A. D.; Pandey , M. K.; Samoluk, S. S.; Abernathy, B.; Agarwal, G.; Ballén-Taborda, C.; Cameron, C.; Campbell, J.; Chavarro, C.; Chitikineni, A.; Chu, Y.; Dash, S.; Baidouri, M. E.; Guo, B.; Huang, W.; Do Kim, K.; Korani , W.; Lanciano, S.; Lui, C. G.; Mirouze, M. ; Moretzsohn, M. C.; Pham, M.; Shin, J. H.; Shirasawa, K.; Sinharoy, S.; Sreedasyam , A.; Weeks , N. T.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, Z.; Froenicke, L.; Aiden, E. L.; Michelmore, R.; Varshney, R. K.; Holbrook, C. C.; Cannon , E. K. S.; Scheffler, B. E.; Grimwood, J.; Ozias-Akins, P.; Cannon, S. B.; Jackson, S. A.; Schmutz, J. 2019. The genome sequence of segmental allotetraploid peanut Arachis hypogaea. Nat. Genet. 51: 877-884.
Cason, J. M.; Simpson, C. E.; Burow, M. D.; Tallury, S.; Pham, H.; Ravelombola, S. W. 2023. Use of wild and exotic germplasm for resistance in peanut. Journal of Plant Registrations. 17(1): 1-25. https://doi.org/10.1002/plr2.20261
de Blas, F. J.; Bressano, M.; Teich, I.; Balzarini, M. G.; Arias, R. S.; Manifesto, M. M.; Costero, B. P.; Oddino, C.; Soave, S. J.; Soave, J. A.; Buteler, M. I.; Massa, A. N.; Seijo, J. G. 2019. Identification of smut resistance in wild Arachis species and its introgression into peanut elite lines. Crop Science. 59:1657-1665. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2018.10.0656
Di Rienzo, J. A.; Casanoves, F.; Balzarini, M. G.; González, L.; Tablada, M.; Robledo, C. W. 2020. InfoStat, versión 2020. Centro de Transferencia InfoStat. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba. Argentina. http://www.infostat.com.ar
García, A. V.; Silvestri, M. C.; Vandecaveye, M. A.; Custodio, A. R.; Moretzsohn, M. C.; Lavia, G. I. 2021. Genomic affinity in hybrids of B-genome Arachis species: new genetic resources toward peanut improvement. Crop Breeding and Applied Biotechnology. 21(3): e38292139. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/1984- 70332021v21n3a48
Giordano, D. F.; Del Canto, A.; Erazo, J. G.; Pastor, N. A.; Crenna, A. C.; Rosso, M.; Torres, A. M.; Oddino, C. M. (en prensa). Fungicide management of late leaf spot and peanut smut. Revista de la Facultad de Ciencias Agrarias. Universidad Nacional de Cuyo. Mendoza. Argentina.
Grabiele, M.; Chalup, L.; Robledo, R.; Seijo, G. 2012. Genetic and geographic origin of domesticated peanut as evidenced by 5S rDNA and chloroplast DNA sequences. Plant Systematics and Evolution. 298: 1151-1165. Doi: 10.1007/s00606-012-0627-3
Gregory, W. C.; Gregory, M. P. 1976. Groundnut. En: Simmonds, N. W. (Ed.). Evolution of crop plants. London. Longman Group Ltd. 151-154.
Harlan, J. R.; de Wet, J. M. J. 1971. Toward a rational classification of cultivated plants. Taxon. 20(4): 509-517.
. Husted, L. 1933. Cytological studies of the peanut Arachis I. Chromosome number, and morphology. Cytologia. 5: 109-117. https://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.5.109
Husted, L. 1936. Cytological studies of the peanut Arachis II. Chromosome number, morphology and behavior and their application to the problem of the origin of cultivated forms. Cytologia. 7: 396-423. ttps://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.7.396
Krapovickas, A.; Gregory, W. C 1994. Taxonomía del género Arachis (Leguminosae). Bonplandia. 8: 1-186.
Marinelli, A.; March, G.; Rago, A. M. 1995. El carbón del maní Thecaphora frezii sobre Arachis hypogaea. Actas VII Congreso de Micología y XVII Jornadas Argentinas de Micología. Argentina.
Oddino, C.; Rosso, M.; Giordano, D. F.; de Blas, F.; Bressano, M.; Soave, S.; Moresi, A.; Seijo, G.; Buteler; M.; Soave, J. 2021. Comportamiento a enfermedades y rendimiento de genotipos provenientes de maníes silvestres. Actas XXXVI Jornada Nacional del Maní. Argentina.
Paredes, J. A.; Cazón, L. I.; Osella, A.; Peralta, V.; Alcalde, M.; Kearney, M. I.; Zuza, M. S.; Rago, A. M.; Oddino, C. 2016. Relevamiento regional del carbón de maní y estimación de pérdidas producidas por la enfermedad. Actas XXXI Jornada Nacional de Maní. Argentina.
Paredes, J. A.; Guzzo, M. C.; Monguillot, J. H.; Asinari, F.; Posada, G. A.; Oddino, C. M.; Giordano, D. F.; Morichetti, S. A.; Torres, A. M.; Rago, A. M.; Monteoliva, M. I. 2024. Low water availability increases susceptibility to peanut smut (Thecaphora frezzii) in peanut crop. Plant Pathology. 73: 316-325. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.13810
Pedelini, R. 2016. Maní, guía práctica para su cultivo. Boletín de divulgación técnica N° 2. 4° Edición.
Rago, A. M.; Cazón, L. I.; Paredes, J. A.; Edwards Molina, J. P.; Conforto, E. C.; Bisonard, E. M.; Oddino, C. 2017. Peanut smut: from an emerging disease to an actual threat to Argentine peanut production. Plant Disease. 101: 400-408.
Robledo, G.; Lavia, G. I.; Seijo, J. G. 2009. Species relations among wild Arachis species with the A genome as revealed by FISH mapping of rDNA loci and heterochromatin detection. Theoretical and Applied Genetics. 118: 1295-1307. doi:10.1007/s00122- 009-0981-x
Robledo, G.; Seijo, J. G. 2010. Species relationships among the wild B genome of Arachis species (section Arachis) based on FISH mapping of rDNA loci and heterochromatin detection: A new proposal for genome arrangement. Theoretical and Applied Genetics. 121: 1033-1046. doi:10.1007/s00122-010-1369-7
Silvestri, M. C.; Ortiz, A. M.; Lavia, G. I. 2015. rDNA loci and heterochromatin positions support a distinct genome type for ‘x = 9 species of section Arachis (Arachis, Leguminosae). Plant Systematics and Evolution. 301: 555-562. doi:10.1007/s00606-014-1092-y
Simpson, C. E.; Starr J. L.; Church, G. T.; Burrow, M. D.; Paterson, A. H. 2003. Registration of NemaTAM peanut. Crop Science. 43: 1561. doi:10.2135/cropsci2003.1561
SISA. 2023. Sistema de Información Simplificado Agrícola. https://www.afip.gob.ar/actividadesAgropecuarias/sector-agro/sisa/informacion-productiva.asp
Smartt, J.; Gregory, W. C.; Gregory, M. P. 1978. The genomes of Arachis hypogaea. 1. Cytogenetic studies of putative genome donors. Euphytica. 27: 665-675. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023701
Stalker, H. T. 1991. A new species in section Arachis of peanut with a D genome. American Journal of Botany. 78: 630-637. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1991.tb12587.x
Stalker, H. T. 2017. Utilizing wild species for peanut improvement. Crop Science. 57: 1102-1120. doi:10.2135/cropsci2016.09.0824
USDA. 2023. United States Department of Agriculture. Peanut explorer. https://ipad.fas.usda.gov/cropexplorer/cropview/commodityView.aspx?cropid=2221000&sel_year=2022&rankby=Production. Consultado 12/09/2023.

Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2018 Revista de la Facultad de Ciencias Agrarias UNCuyo

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 3.0.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.










.jpg)




