Enterococcus gallinarum CRL 1826 as a probiotic for ranaculture: in vitro safety, technological, and physiological properties
Keywords:
Enterococcus gallinarum, safety characteristics, lyophilization, probiotics for aquaculture, bullfrogAbstract
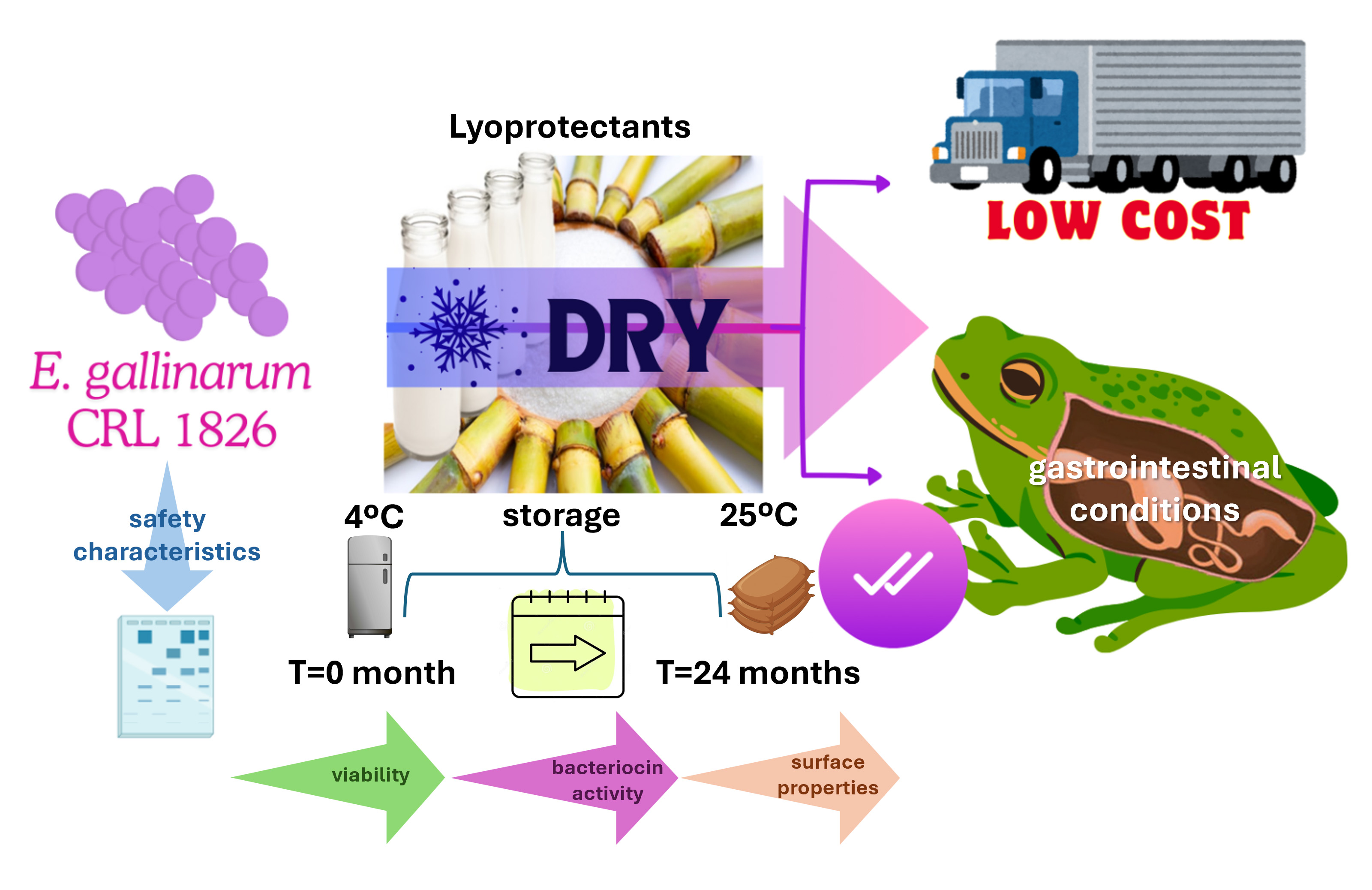
This study aimed to progress in designing a probiotic containing autochthonous Enterococcus gallinarum CRL 1826 for application during the life cycle of Lithobates catesbeianus in hatchery conditions. We assessed bacterial resistance to chemotherapeutics used in ranaculture, the presence of genes encoding virulence factors (VF) and vancomycin resistance, and bacterial survival and maintenance of beneficial properties after freeze-drying and storage. The strain exhibited resistance to antiseptics, sensitivity to most chemotherapeutics, presence of vanC, and absence of VF genes. It demonstrated resistance to freeze-drying and the highest survival when using skim milk+sucrose and storage at 4°C for 24 months. It also displayed bacteriocin activity against Listeria monocytogenes. Pre-lyophilized and lyophilized cultures grew/resisted individual gastrointestinal conditions and simulated gastrointestinal digestion, keeping bacteriocin activity and surface properties. For the first time, we demonstrated that E. gallinarum CRL 1826 is a safe bacterium with technological and physiological properties that would allow bullfrog gut colonization. These studies are essential for progressing towards selecting E. gallinarum CRL 1826 as a probiotic to prevent epizootics during bullfrog breeding and control foodborne bacteria, potentially improving growth performance of L. catesbeianus.
Highlights:
- Enterococcus gallinarum CRL 1826 was sensitive to chemotherapics used in ranaculture.
- The strain did not display virulence and transferable vancomycin resistance genes.
- The dried strain showed great survival and bacteriocin activity for 24 months’ storage.
- The LAB resisted the gastrointestinal conditions and kept its bacteriocin activity.
Downloads

Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2018 Revista de la Facultad de Ciencias Agrarias UNCuyo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan las Políticas Editoriales.










.jpg)




